Information Retrieval is the process of finding the most relevant information from a large collection of data (set of documents) for a given user query. Information Retrieval is the back bone of several systems such as
- Web Search
- Email Search
- Library catalogs
- ChatGPT etc
In this post, we will be learning about the following topics.
- General Search Process
- Document Indexing – Inverted Index
- Text Processing
- Types of Retrieval Models
- Metrics to Evaluate Search
General Search Process
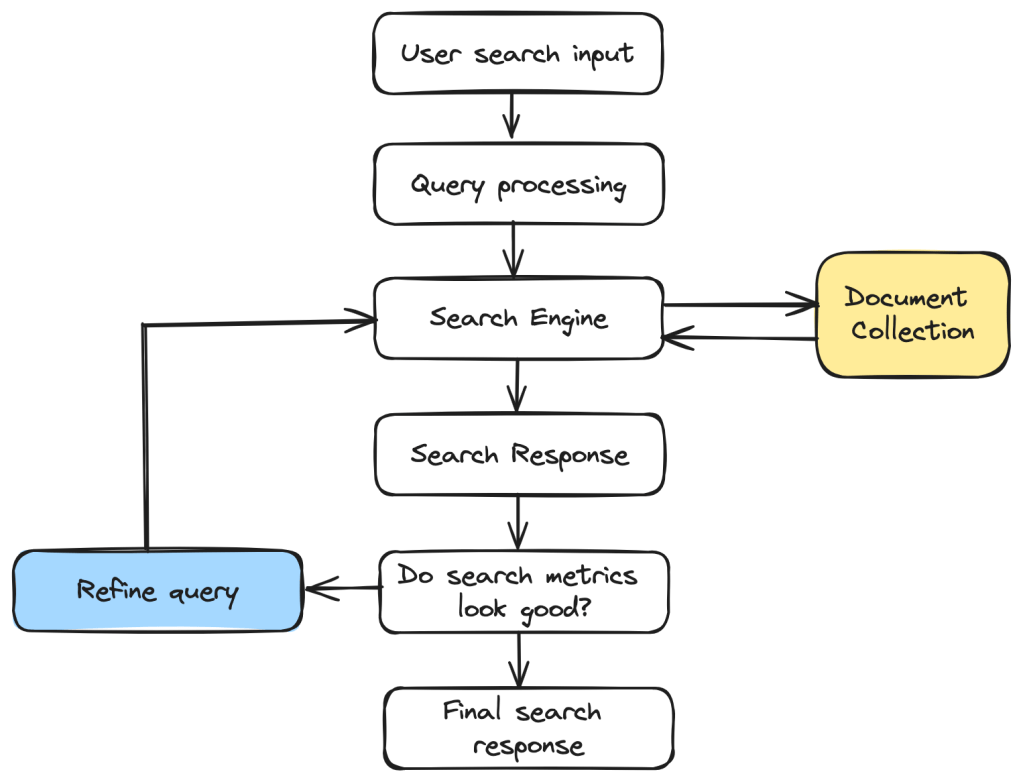
The following diagram gives an idea of the overall search process. When a user searches for a certain information, that information is transformed into a query that can be understood and processed by the search engine.
The query is then processed by the search engine to retrieve the most relevant documents from the collection. Certain metrics are used to evaluate the search response and if the results are not satisfactory, we refine the query further and reprocess it.
Document Indexing – Inverted Index
In order to retrieve information as fast as possible, we need to index the documents efficiently. We build what is called an “Inverted Index” for fast look up of documents that are most relevant to a search input.
An inverted index is a mapping of the different terms in a large collection to a list of documents in which the term occurs. The document is usually referred to by the document ID aka doc ID. The list of doc IDs is called a postings list. A variable length postings list is used to keep it updated as documents get updated.

Text Processing
Before building the inverted index, a number of text processing steps are performed on the documents in order to retrieve information effectively and minimize storing unnecessary words.
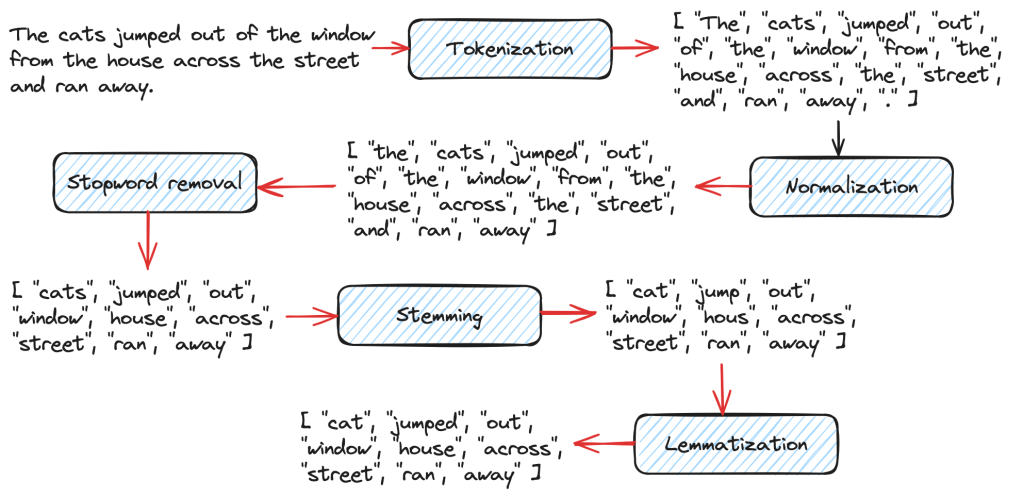
Tokenization
This step breaks down the given documents or text into individual words called tokens.
Normalization
At this step, extraneous details such as caps lock, punctuation etc are removed.
Remove Stopwords
There are many words such as “the”, “a” etc which don’t have any significance, so these are removed.
Stemming and Lemmatization
Stemming removes unwanted prefixes and suffixes from words. For ex: running -> run, books -> book.
Lemmatizers on the other hand, transform a word to its language-specific dictionary form. This produces more linguistically accurate words.
Types of Retrieval Models
Boolean Retrieval Model
This model can process Boolean queries that involve Boolean operators such as AND, OR, NOT etc. The inverted index is built based on the presence of terms in documents. This is simple and pretty popular but it cannot process queries that require contextual understanding.
Probabilistic Retrieval Model and BM25
This model ranks the documents based on the probability of their relevance to the search query. Okapi BM25 where BM stands for “Best Matching” is one of the most popular algorithms under the Probabilistic Retrieval Model. It calculates the document scores using various parameters such as term frequency, inverse document frequency, document length normalization etc.
Vector Space Model
In this model, data and queries are transformed into vectors in a multi-dimensional space. The number of dimensions will depend on the features used to represent the data. There are various distance metrics that can be used to compute the distance between points that capture semantic similarity but cosine distance is a popular one. This is a great model to capture contextual information.
Latent Semantic Indexing
This model captures latent semantic relationships between documents and terms using Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) to identify underlying concepts within a body of text. SVD is a technique to reduce dimensionality while preserving contextual information at the same time.
Neural Information Retrieval
NIR can capture complex semantics in text data thereby improving the accuracy and relevance of search. This model uses Neural Networks to retrieve highly relevant documents during search.
Metrics to Evaluate Search
There are two popular metrics to evaluate how good search results are. Although there are many others that we will be looking into in the future, these two are important.
- Precision – This metric refers to the fraction of documents retrieved by search that are relevant to the user query. This points to the accuracy of the search results. Precision values are between 0 and 1 where 1 means a perfect accuracy score where all the documents were relevant to the search query.
- Recall – This metric refers to the fraction of relevant documents retrieved by search from the total number of relevant documents in the collection. Recall values also range from 0 to 1 with 1 meaning that all the relevant documents in the collection were retrieved by the search operation.
Hope you enjoyed this Introduction to Information Retrieval post. Let us continue exploring various topics related to Information Retrieval and Semantic Search in future posts. Have a wonderful day!

